نتائج البحث (256,369)
3 WAYS MEDICAL APPOINTMENT SCHEDULING SOFTWARE BENEFITS THERAPISTS.pdf
jaydenhenrii
Apollo, the patient appointment scheduling software can provide great conveniences and benefits not only to patients but also to therapists who choose to invest in them.

Mahadev Book and the Rise of Smarter Online Platforms
The digital world is changing fast. Users now expect platforms to be simple, fast, and reliable. Mahadev Book understands this shift. That is why it continues to evolve as part of the rise of smarter online platforms. Its focus remains on usability, performance, and user satisfaction.

Best Electrician in Hyderabad.pdf
Admin
Best Electrician in Hyderabad For all your electrical needs in Hyderabad, look no further than the Toskie App to connect you with the best electricians in the city. Whether it's a minor repair, a major electrical project, or installation work, our platform offers a curated list of experienced and reliable electricians to ensure your electrical systems are in safe hands. Using the Toskie App, you can easily find electricians with the expertise to handle various electrical issues, from wiring and lighting to appliance installations. Our goal is to make the process of finding and hiring a skilled electrician convenient and stress-free. The app allows you to browse through profiles, read customer reviews, and choose the electrician that best fits your requirements. We understand the importance of timely and efficient electrical services, and our electricians are committed to delivering top-notch service with a focus on safety and quality.

Ventajas del Alquiler esqui Sierra Nevada frente a comprar tu propio equipo
Ventajas del Alquiler esqui Sierra
Si estás planeando una escapada a la nieve, Sierra Nevada es uno de los destinos más impresionantes de toda España. Sus pistas bien cuidadas, su clima excelente y su ambiente familiar la convierten en el lugar perfecto para disfrutar del esquí. Pero antes de lanzarte a las pistas, es importante contar con el equipo adecuado. Aquí es donde entra en juego el Alquiler esqui Sierra Nevada, una opción cómoda https://skirenting.com/es/estaciones/alquiler-esqui-sierra-nevada/

The Enduring Impact of Italian Marble in Indian Interior Design
Inani Stones
At first sight when thinking about Indian interior design, one company comes to mind – Inani Stones. This is one of the companies that provide the best Italian marble which makes it to be highly preferred when it comes to interior design projects in the country. Here in this article let us look at the cost of the Italian Marble price in India point of inception and why the same from Inani Marbles is preferred by every Interior Decorator as a homeowner. Visit Website - https://inanistones.com/italian-marble-price-in-india.php #italianmarblepriceinindia #inanistones

logistics-company-in-saudi-arabia
Dar Ul Abideen Logistics Services empowers organizations through flexible warehousing and supply chain solutions built for precision and reliability. Our advanced facilities and digital systems streamline storage, distribution, and fulfillment—enabling safer operations and sustainable logistics growth across Saudi Arabia.

logistics-in-saudi-arabia-business-guide
Dar Ul Abideen Logistics Services supports Saudi businesses with customized warehousing and integrated supply chain management. By combining secure storage infrastructure with smart systems, we enhance inventory accuracy, distribution efficiency, and fulfillment speed—driving consistent logistics performance across the Kingdom.

logistics-company-in-riyadh-presentation
Through customized warehousing and supply chain strategies, Dar Ul Abideen Logistics Services helps businesses achieve faster, safer, and more accurate operations. Our secure, high-volume warehouses and intelligent logistics platforms strengthen supply chain performance and support long-term growth across Saudi Arabia.

iyadh-logistics-companies-overview
With tailored warehousing and supply chain services, Dar Ul Abideen Logistics Services helps companies operate more efficiently and securely. Our high-capacity warehouses and intelligent logistics systems optimize inventory flow, streamline fulfillment, and support scalable growth throughout Saudi Arabia.

3pl-logistics-services-in-saudi-arabia
Dar Ul Abideen Logistics Services delivers customized warehousing and supply chain solutions that improve speed, safety, and operational accuracy. Our secure, large-scale facilities and technology-driven systems simplify inventory control, distribution, and order fulfillment—helping businesses build reliable logistics networks across Saudi Arabia.

Metrofino BTM - Crypto ATM in Michigan
Are you looking for a convenient and reliable way to access cryptocurrencies in Michigan? Look no further than Metrofino BTM Crypto ATMs. With our cutting-edge technology and user-friendly interface, we bring you a seamless and secure experience for buying and selling cryptocurrencies.

Houston Texas Dunk Tank Rentals.pdf
PC
Need to Rent a Dunk in Houston Texas? www.BoogieBouncehouston.com offers dunk tank rentals for your convenience.

Family Vacation Deals To Los Angeles
family vacation deals to los angeles
Plan your next adventure with family vacation deals to Los Angeles. Explore Hollywood, beaches, and fun family attractions for less!

Gdzie Sie Robi Badania Na Prawo Jazdy.pdf
PC
kupić prawo jazdy - Mieszkasz w polsce i szukasz miejsca gdzie bez problemu kupisz prawo jazdy?Skorzystaj z naszych usług i ciesz się nowym prawem jazdy już

SAP C_THR70_2309 Certification Guide: Expert Tips, Full Syllabus and Latest Questions
www.Erpprep.com
Start Here--- https://bit.ly/4b148IU ---Get complete detail on C_THR70_2309 exam. You can collect all information on C_THR70_2309 tutorial, practice test, books, study material, exam questions, and syllabus. Firm your knowledge on SuccessFactors and get ready to crack C_THR70_2309 certification. Explore all information on C_THR70_2309 exam with number of questions, passing percentage and time duration to complete test.

Bellanic Brings You its Trendiest Design in Name Necklaces
Bellanic
Find information on Bellanic bringing you its trendiest design in name necklaces. For more details, visit: Bellanic.com.

Are You Ready to Pass the Broadcom 250-554 Exam?
Certfun.com
Start Here--- https://bit.ly/3Tu0UY5 ---Get complete detail on 250-554 exam guide to crack Technical Specialist of Symantec Web Security Service - R1.2. You can collect all information on 250-554 tutorial, practice test, books, study material, exam questions, and syllabus. Firm your knowledge on Technical Specialist of Symantec Web Security Service - R1.2 and get ready to crack 250-554 certification. Explore all information on 250-554 exam with number of questions, passing percentage and time duration to complete test.

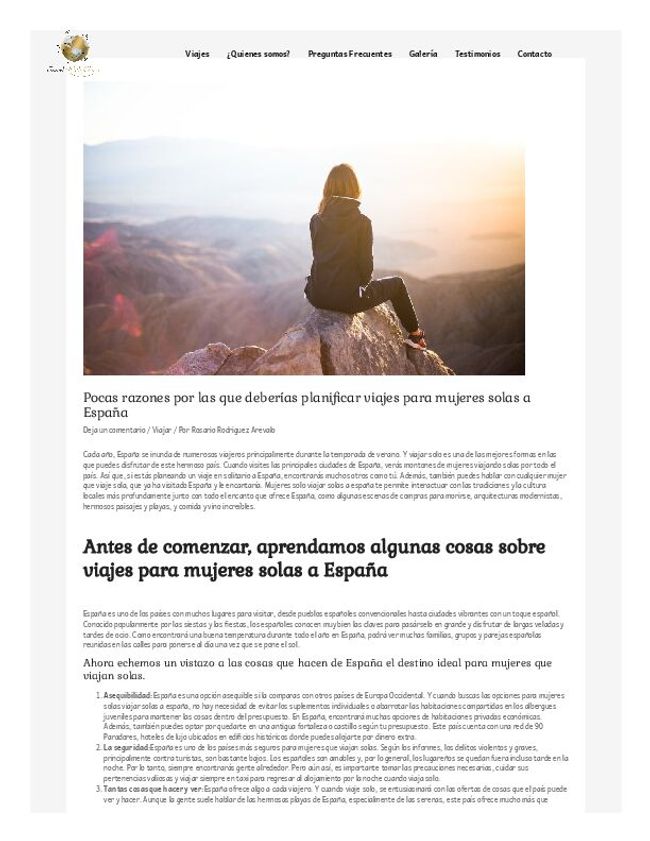
Mujeres solo viajar solas.pdf
Travelwithcharo.es
Mujeres solo viajar solas, Cada año, España se inunda de numerosos viajeros principalmente durante la temporada de verano. Y viajar solo es una de las mejores formas en las que puedes disfrutar de este hermoso país. Cuando visites las principales ciudades de España, verás montones de mujeres viajando solas por todo el país. Así que, si estás planeando un viaje en solitario a España, encontrarás muchos otros como tú. Además, también puedes hablar con cualquier mujer que viaje sola, que ya ha visitado España y le encantaría. https://www.travelwithcharo.es/mujeres-solo-viajar-solas-a-espana/
Miami: Iconic Luxury Living, Branded Residences, and Prime Investment Appeal
Eduardo
Brickell’s rise as one of the most powerful real estate markets in the United States continues to accelerate in 2025. Once known primarily as Miami’s financial district, Brickell has evolved into a global lifestyle destination where luxury condos, five-star hospitality, and international investment converge.

Making the Right Choice 4 BHK Flats in Gurgaon.pdf
Discover your dream home with Sheerbulls India. Making the right choice is crucial, and our curated selection of 4 BHK flats in Gurgaon ensures a perfect blend of luxury and comfort. Explore flats for sale in Gurgaon's prime locations, guided by our expertise in real estate. Your ultimate residence awaits.












